Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Virus Skin Infection
Virus skin infections are skin conditions caused by one or more viruses. They affect people of all ages and can affect one or more skin layers. In worse situations, they enter the bloodstream.
The skin is the largest organ in the body. It is also the first line of defence against infection. The skin is made up of layers. They all have different functions.
The epidermis is the first layer of the skin outside. It protects the body against different forms of virus from the surrounding. The dermis is the next layer which provides nutrition for the epidermis. The subcutaneous tissue is the last layer which acts as a shock absorber for the skin, stores energy and regulates body temperature.
Causes Of Skin Infection
There are viruses in the air and the surrounding. There are viruses on the skin. However, the skin is safe as long as the skin is not broken. Virus can enter the skin from cuts or when there are allergic skin diseases such as eczema. In some cases, large virus colonies in the skin can cause skin infection.
A virus that gains access into the skin will do well to migrate to the layer with the best condition and start to multiply. This multiplication results in an increased need for more nutrients from under the skin and more space. This leads to different types of skin condition.
Virus Skin Infection
There are thousands of species of virus that can cause skin infections. Some can cause more than one type of infection. But it is easy to diagnose a virus skin infection from other types of skin infection.
Read Also: Drugs for treating bacteria skin infection
Virus skin infection often presents with small or large blisters coupled with fever.
Treatment often consists of topical cream or ointments. Severe cases rarely occur. But if they do, oral or injectable antivirus does the work. Some may require minor surgery that can be done even without anesthesia. Vaccines are available for some virus infections and do well to prevent or treat the disease.
Diagnosis/Test
Virus skin infection can be diagnosed by merely doing skin examination. The room should be well lit and without shadow. The area of the body uncovered and the skin examined with a magnifying len.
Last resort is to request for a laboratory diagnosis. Most virus skin infections can be diagnosed without it. However, two major laboratory investigations for virus skin infection is skin biopsy or cell culture.
Types Of virus Skin Infection
There are different viruses that cause skin infections. They are classified under six categories.
Shingles
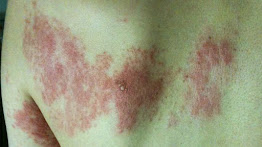
Shingles is a disease caused by the virus varicella-zoster. This is the same virus responsible for chickenpox disease. It affects people who have had chickenpox before. It goes dormant in the body in the neuron and comes back not as chicken pox but now as shingles with different symptoms from chicken pox. It is also called herpes.
It is a disease that affects one million people every year in the United States of America (USA). From the research, one in three persons get complications. That is about 30 percent. The disease clears within two to three weeks and rarely occurs again due to immunity. It is found in the eyes, back, face, mouth, buttocks, torso (spine) chest, scalp (permanent baldness) and eyes (blindness).
 |
| Shingles image |
Shingles image gallery
Symptoms
It begins with a red skin rash that is accompanied by pain, itching and burning. The rash is like a strip of patches located on one side of the body only. It affects the back, torso, neck or face. The rash becomes fluid-filled.
Some symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, fatigue and muscle weakness rarely occur. Complicated cases are characterized by pain or rash in the eye that can lead to blindness, loss of hearing, dizziness or Ramsay hunt syndrome which is associated with loss of taste. Others are pneumonia, encephalitis and meningitis which could be extremely fatal. This is common in situations whereby there is secondary infection in which the skin becomes red, swollen, or warm to the touch.
Pain occurs in the nerve of the chest or neck, face or lower back. The pain is triggered by the reactivation of the virus changing how sensory neurons work.
Causes
It is caused by varicella-zoster virus. It is the same virus that causes chicken pox. It is the dormant form in the neuron that re-emerge as shingles. And this happens after some years. It is believed that a weak immune system is responsible for the re-emergence of the virus in the form of shingles. Other factors thought to be responsible are age (above 60 years), chemotherapy and emotional stress.
Also, It is not contagious. It is spread through contact with oozing blisters by someone who had never had chickenpox before. The blisters are not contagious when they are covered or had form scab or clear rash.
Stages Of Shingles
The shingles course of infection is between three to five weeks. It has three stages:
1. Tingling, burning, numb or itchy sensation under the skin
2. Red rash that begins after five days with fluid-filled blisters oozing that is accompanied by fever, headache and fatigue
3. Blister begin to dry up and form scab
Diagnosis
Use a sterile swab to collect samples of tissue or fluid for analysis.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Shingles
Drugs
There is no cure for shingles. Treatment is based on easing symptoms and to shorten the duration of infection. Some antivirals have been shown to help reduce pain associated with shingles and speed recovery. They are oral acyclovir, valacyclovir and famciclovir taken two to five times a day. The dose is standard doses with no alterations.
Antiinflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen taken orally help to relieve pain and inflammation associated with shingles. Another drug that is used for pain is analgesic (paracetamol) and narcotic (codeine). Also, anticonvulsant or tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline) treat pain when taken orally once or twice daily. However, one drug for pain is enough rather than a combination of drugs.
Numbing cream and patches like lidocaine also reduce pain when applied topically. Capsaicin topical cream helps to reduce the risk of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia that occurs after recovery. Antihistamine such as oral loratadine takes care of the itching and it is safe during pregnancy. Antiviral and paracetamol is also safe in pregnancy.
Some home remedies include vitamin A supplement orally. Also, vitamin B12, vitamin C, and vitamin E with amino acid help to reduce the effect of the virus when taken orally. Vitamin A, B12 and E can be applied on the body.
Vaccines
Zostavax and Shingrix are two vaccines approved for the prevention of shingles in adults above 50 years of age. Zostavax is 51 percent effective in preventing shingles and is made from a live weakened virus.
Shingrix is a recombinant vaccine which is 90 percent effective in preventing shingles with a long duration of immunity. First dose and second dose is given eight weeks apart. It is approved for use in adults above 50 years of age.
Shingles vaccine should be avoided in those who had reaction to the first dose, allergic to one or more of its components, neomycin, gelatin, currently have shingles, pregnant or breastfeeding, and had a negative test result to varicella-zoster virus. Also, avoid in people with temperatures above 38.5°c and weakened immune systems due to drugs, disease or organ transplant.
Side effects of shingles vaccine are itching, soreness, swelling, redness with headache, muscle pain, headache, fever, stomach pain, nausea and vomiting. Anaphylaxis has been reported in some cases. These side effects last between two to three days. They can be relieved with pain medication.
Chicken Pox
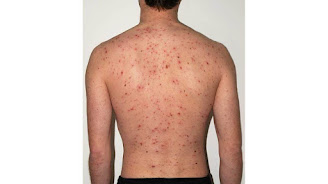
It is also called varicella. It is caused by a virus called varicella-zoster virus which is the same virus responsible for shingles. It appears as itchy red blisters that appear all over the body. It is more common in children.
Symptoms
Symptoms do not manifest after Infection not until after between seven to 21 days. Others are fever, headache and loss of appetite that may last for a few days. After these symptoms subside within two days, the body develops red or pink bumps. The bump becomes blister filled with fluid that leaks. At long last, the bump becomes crusty, scabs over and begins to heal. It heals within one to two weeks.
Bumps appear at different times and not at once. Before it scabs all over with crust, it becomes very itchy. It takes fourteen days for the symptoms to disappear completely.
Complications
Complications are common in children, older adults, those with weak immune systems and pregnant women. Babies born by infected pregnant women can experience intellectual disabilities, eye problems, small head and poor growth
 |
| Chicken in adult |
Image gallery of chicken pox
Cause
It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread through saliva, cough and sneeze of infected persons. Infected people become contagious around 48 hours before rash develop and remain contagious until after all the blisters have scabbed over. Contact with the fluid of the blister is also part of the mode of transmission. Babies acquire passive immunity during birth and breastfeeding that last up to three months.
Diagnosis
Laboratory test based on blood or culture of lesion.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Chicken Pox
There is no treatment available. Treatment is managing symptoms.
Drugs
Intravenous (IV) Immunoglobulin is effective if administered within the first 24 hours after a rash appears. After that, managing the symptoms is the goal of therapy. Oral antiviral like acyclovir, famciclovir and valacyclovir can slow down viral activities. Oral antihistamine like loratadine and topical ointment like calamine lotion is effective in relieving itching.
Vaccine
Vaccine is available and it is effective for preventing up to 80 percent of infection. A starting or loading dose is given at between twelve to fifteen months of age and a maintenance dose by four to six years. The age between three months to twelve months is the dangerous period when the child has passed the duration of passive immunity from mother and not up to the age to receive a vaccine. That is when most modern infection takes place.
For adults who missed the childhood immunization programme, catch up doses are available. The vaccine is effective in reducing symptoms after getting the virus for those who have never been vaccinated against chickenpox and vaccinated during the course of the disease.
Molluscum Contagiosum
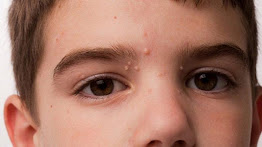
This is a viral infection characterized by benign raised bumps or lesions of the upper skin layer. The bumps are painless which disappear on their own without leaving a scar. The bumps stay between two months to as long as four years.
 |
| Molluscum Contagiosum |
Image gallery of Molluscum Contagiosum
Symptoms
It takes about two to seven weeks for symptoms to manifest and sometimes six months. It begins with a small group of lesions. The lesions can form a group of patches up to twenty. They are very small, shiny and smooth in appearance. Flesh-coloured white or pink, firm and shaped like a dome with a dent or simple in the middle. It is the size of a head of a pin and eraser of a pencil which is 2-5 mm in diameter. It is filled with a central core of waxy material and spread everywhere in the body except the sole of the feet and the palm. In children, it is most common in the face, abdomen, torso, arms and legs and the inner thighs, genitals and abdomen of adults.
Immunocompromised patients may have lesions as large as 15 mm in diameter.
Cause
It is caused by a virus molluscum contagiosum and spreads by direct contact with an infected person or infected objects such as towels or clothes. Another means of transmission is sex.
Risk Factors
1. Children between one to ten years of age
2. Tropical climates
3. Atopic dermatitis
4. Weak immune system
Diagnosis
Skin scraping for biopsy
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Molluscum Contagiosum
Treatment should begin if the lesions are large and/or located on the face and neck, atopic dermatitis present and it is spreading.
1. Cryotherapy is the best treatment. It is the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze each bump
2. Cantharidin cream comes from green blister beetles. It is used when cryotherapy fails. It causes skin to blister.
3. Laser therapy is use to destroy each bump
4. Topical creams containing acid is use to induce peeling of the top layers of the skin
5. Trichloroacetic topical application for peel
6. Podophyllotoxin (PTI) is a medical cream
7. Curettage the bumps to pieces and then scrape it off
8. Imiquimod is an immune response modifier. It works by increasing the activity of the body's immune system
Antivirals are suitable for those with Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) as they may not need extra therapy. In all, the use of anaesthesia is needed because most of the process is painful. Treatment can last between three to six weeks. Heals within six to twelve months. And there is a possibility of re-infection.
Warts
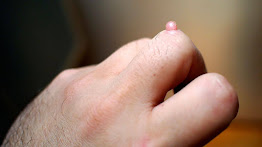
Wart is a skin condition caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV). Wart is not a new disease as it was mentioned some years ago by the popular writer Williams Shakespeare and found in a 3000 years old mummy. They are not dangerous. They call for attention because of the pain and the distortion it causes the sufferer.
There are more than ten types of HPV. They are almost all harmless if they appear on the skin of the leg or hand. The dangerous ones are those that occur around or in the genital (genital warts) which can lead to genital cancer.
 |
| Wart |
Classification
They are classified based on the location they appear and their shape.
1. Common warts: affects the fingers and toes and appear with rough greying and rounded tops.
2. Flat wart: appear in the face, thighs or arms. They appear as small flat scrap tops with pink, brownish or yellow colour.
3. Plantar wart: found under the sole of the feet and grows into the skin and not an outward bump. Surrounding it is a layer of hard skin. That means that it is like a hole or well under the skin.
4. Filiform wart: located around the mouth or nose, neck and under the chin. They appear small with a shape that looks like a tiny flap or Tay of skin. It mimics the colour of the skin that it is difficult to distinguish.
5. Periungual wart: this type attacks the toe and fingernails. It is very painful and eventually affects nail growth.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Wart
It heals on its own without treatment in most cases. However, medical care is needed for warts that affect the genitals, mouths, nostrils, warts that lead to bleeding or those with signs of secondary bacteria infection. The signs are pus, scabbing, colour change or compromised with other diseases like diabetes, HIV/AIDS or immunodeficiency conditions.
1. Dimethyl ether and propane (cold air) is sprayed onto the wart.
2. Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide) is another method of freezing wart but it is only advisable for warts not in sensitive parts of the body. The side effects of this treatment method include damage to nerves, slow healing, ulcer formation, skin lesions and long lasting sore or altered pigmentation.
3. Salicylic acid cream is another effective method but requires soaking in water for 15 minutes before application all the time.
4. Duct tape involves covering the wart with a small piece of duct tape for several days, then soaking the wart before rubbing it off. This approach requires repeated rounds of treatment to work.
5. Surgery is the last resort. An anaesthetic is needed.
Preventing measures involve personal hygiene and use shoes or slippers in public bathroom facilities.
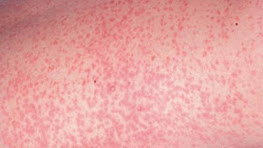
Measles
Measles is a very common viral infection of the skin. It is also called rubeola. It is very deadly and is responsible for about 110000 deaths worldwide in 2017. It is common in children under the age of five years. And there is life time immunity for those who survived the infection.
 |
| Measles |
Symptoms
Symptoms manifest from ten to twelve days after exposure to the virus. Symptoms include cough, fever, runny nose, red eyes, sore throat and white spots inside the mouth. Later, a rash that spread all over the body from the head down appeared on day 14 from the day of exposure. This rash can last for seven days.
Complications of measles include pneumonia, encephalitis, deafness and blindness. In pregnant women, it can lead to still birth, low birth, preterm labour and miscarriage.
Cause
It is caused by the virus paramyxovirus. It begins from the respiratory system before affecting the skin. Out of the 24 known species of the virus, only six are in circulation. The virus only survives in human hosts.
The virus is spread through droplets or aerosols of an infected person. This occurs when the person coughs or sneezes. The virus survives up to two hours outside an infected person and it is highly contagious. There is a 90 percent possibility of getting infection in an area where it is dominant. People become contagious about four days even before development of symptoms. And they can remain contagious for another four days even after the symptoms have subsided.
The virus is more complicated in children, pregnant women and those with weak immune systems.
Classification Of Measles
1. Classical and congenital measles occur at birth
2. Atypical measles occurs in people who receive the measles vaccine in 1963-1967. When exposed to measles, they come down with high fever, rash and pneumonia.
3. Modified measles occur in people who got post exposure immunoglobulin and infants passive immunity. Their symptoms are always mild.
4. Hemorrhagic Measles come with high fever, seizures and bleeding into the skin and mucous membranes.
Diagnosis
Blood test
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Measles
Drugs
Immunoglobulin is another form of treatment taken before six day of exposure. Paracetamol is to reduce fever and mild pain while fluid is to replace lost fluid. Humidifier is to soothe cough symptoms and sore throat. Since vitamin A deficiency occurs in measles patients, vitamin A is needed but how it helps reduce the virus activity is not clear. Children develop immunity during childbirth and breastfeeding.
Vaccines
The vaccine was approved in 1963. It is assumed that all those who lived before that year have had and survived the infection. So therefore, they don't need a vaccine since they will become immune to the infection. Measles vaccine given within 72 hours of exposure can shorten the duration and prevent complications. It is 97 percent effective. The first dose is given at twelve months of age. A maintenance dose is given at 4-5 years.
Read Also: Antibiotics stewardship
There are two types of measles vaccine. They are:
1. MMR is a combination of measles, mumps and rubella vaccine
2. MMRV is a combination of the above with chicken pox vaccine.
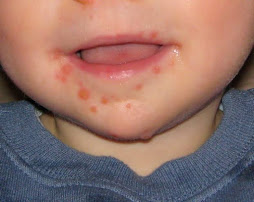
Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease
Just as the name goes, this skin infection affects the mouth, hand and foot. It is caused by enterovirus of which the most common species is Coxsackie A16 virus. The infection is common in children below the age of five. However, it does not spare adults.
 |
| Hand, foot and mouth disease Source: Wikipedia |
Symptoms
It is a mild condition that goes away on its own within several days. Symptoms begin to manifest from day three to seven after exposure to the infection in the form of fever and sore throat. It is characterized by blisters or painful red sore in the mouth and a red rash on the hands and feet. Others are fever, poor appetite, sore throat and headache irritability.
Complications
1. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)
2. Degeneration of nerve
Cause
They are caused by enterovirus of the species Coxsackie virus. They are highly contagious and can spread from person to person through direct contact with an infected person. Contaminated surface by faeces, saliva and respiratory droplets can expose healthy persons to the virus. Infected persons are contagious at first week of exposure and continue for a few weeks after the infection is cleared
Diagnosis
A throat or stool sample
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease
Over the counter (OTC) ointment such as calamine lotion soothe lesions and rash. Paracetamol and other non steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) like ibuprofen relieve headache while syrups or lozenges are for sore throat. Mouths are antibacterial mouthwash or warm salt water also for the sore throat. Vitamin A as part of treatment is also encouraged in oral form.

Comments
Post a Comment
Please have your say