Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Bacteria Skin Infection
Bacteria skin infection are skin conditions caused by one or more bacterias. They affect people of all ages and can affect one or more skin layers. In worse situations, they enter the bloodstream.
The skin is the largest organ in the body. It is also the first line of defence against infection. The skin is made up of layers. They all have different functions.
The epidermis is the first layer of the skin outside. It protects the body against different forms of bacteria from the surrounding. The dermis is the next layer which provides nutrition for the epidermis. The subcutaneous tissue is the last layer which acts as a shock absorber for the skin, stores energy and regulates body temperature.
Causes Of Bacteria Skin Infection
There are bacteria in the air and the surrounding. There are bacterias on the skin. However, the skin is safe as long as the skin is not broken. Bacteria can enter the skin from cuts or when there are allergic skin diseases such as eczema. In some cases, large bacteria colonies in the skin can cause skin infection.
Read Also: Eating stony rice does not cause appendicitis
Risk Of Bacteria Skin Infection
1. live in a warm, humid climate 2. have diabetes 3. are undergoing dialysis 4. have a compromised immune system, such as from HIV 5. haves skin conditions such as eczema, dermatitis, or psoriasis 6. have a sunburn or other burns 7. have itchy infections such as lice, scabies, herpes simplex, or chickenpox 8. have insect bites or poison ivy 9. play contact sportsBacteria that gained access into the skin will do well to migrate to the layer with the best condition and start to multiple. This multiplication results in an increased need for more nutrients from under the skin and more space. This leads to different types of skin condition.
Bacteria Skin Infection
There are thousands of species of bacteria that can cause skin infections. Some can cause more than one type of infection. But it is easy to diagnose a bacteria skin infection from other types of skin infection.
Bacteria skin infection often presents with small red bumps that slowly increase in size. In some cases, it is filled with whitish or coloured pus.
Treatment often consists of topical cream or ointments. Severe cases rarely occur. But if they do, oral or injectable antibacterial does the work. Some may require minor surgery that can be done even without anesthesia.
Diagnosis/Test
Bacteria skin infection can be diagnosed by merely doing skin examination. The room should be well lit and without shadow. The area of the body uncovered and the skin examined with a magnifying len.
Last resort is to request for a laboratory diagnosis. Most bacteria skin infection can be diagnosed without it. However, two major laboratory investigations for bacteria skin infection is skin biopsy or cell culture.
Types Of Bacteria Skin Infection
There are different bacterias that cause skin infections. They are classified under four categories.
Cellulitis
This is a bacteria skin infection caused by staphylococcus and streptococcus that appears as a red and swollen area. It feels hot and tender to touch. The redness and swelling can spread quickly. It appears everywhere but more commonly found on the leg. Severe cases get to lymph nodes and the bloodstream which can be very dangerous.
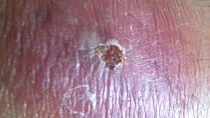 |
| Cellulitis image |
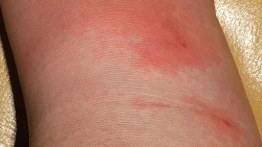 |
| Cellulitis hand |
Check Gallery for more images
Minor Symptoms
1. Pain and tenderness in the affected area
2. Fever
3. Skin sore and rash that grows quickly
4. Red or inflammation of the skin
5. Feeling of warmth in the affected area
6. Light, glossy, swollen skin
7. Abscess with pus
Major Symptoms
1. Shaking
2. Chills
3. Fatigue
4. Feeling ill
5. Dizziness
6. Lightheadedness
7. Muscle ache
8. Warm skin
9. Sweating
10. Drowsiness
11. Lethargy
12. blisters
13. Red streaks indicate it is spreading
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that is susceptible to many antibacterial substances. They include penicillin G, erythromycin, dicloxacillin, amoxicillin, cephalexin, clindamycin, azithromycin or clarithromycin. Oral antibacterial for 5-10 days with aspirin for swelling does take care of. However, when oral antibacterial is not fast enough, intravenous injection should be used. Surgery is to drain the pus. The leg should be raised above heart level.
Impetigo
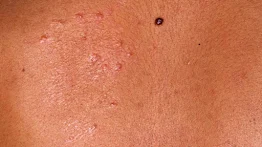
It is another bacteria infection caused by staphylococcus aureus or streptococcus pyogenes. It affects the arms, face, and legs epidermis. It is contagious and very common in children between the age of two to five years.
There are two types of impetigo. They are primary impetigo which affects healthy skin. Secondary impetigo affects broken skin. Both types are common in warm and humid climates.
 |
| Impetigo image |
 |
| Impetigo picture |
Symptoms
It begins with a rash like eczema. Then it forms reddish sores in the skin. They grow into blisters, pus filled which burst forming a yellowish crust. Not all develop blisters.
The sore can be itchy and occasionally painful. After the crust phase, they form marks that fade without leaving a scar.
Impetigo in infants occurs around the diaper area or in skin folds. Large fluid filled blister bursts leaving a scaly rim called a colarecter. It can involve swollen glands.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Impetigo
Topical cream or ointment is good for impetigo cure. Mupirocin cream or ointment is very effective applied morning and night. The skin should be disinfected by washing with soap and water before application. Where topical is not quick enough, oral amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, clindamycin, cephalexin or cefuroxime does the job but side effects are high. Cloxacillin orally for seven days while children can be given intravenous injection. Cefalexin orally for seven days is also recommended where there are absences. It heals within seven to ten days. But the full dose of the antibacterial must be completed even when there seems to be remarkable improvement within days.
Complications In Adults
Cellulitis, sepsis, lymphangitis and acute post streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Classification Of Impetigo
Non bullous: it is caused mainly by staphylococcus aureus which is more common with less symptoms. It begins with reddish, itchy sores around the mouth and nose. The sore breaks open leaving red and irritated skin around them. A brownish yellow crust forms. When the crust heals, there are reddish spots that heal and don't leave scars.
Bullous: is also caused by mainly staphylococcus aureus and usually form large blisters or bullous filled with a clear fluid that become darker and cloudy. The blisters start on unbroken skin and are not surrounded by reddish areas. The blisters become limped and clear and then burst open. A yellowish crust sore forms over the area where the blister breaks open. The blister usually leaves no scars behind when they heal.
Erythema: is more serious and less common. It goes deep into the skin. It forms painful blisters on the skin of the buttocks, thighs, legs, ankles and feet. The blister turns into a pus-filled sores with a thicker crust. Often the skin around the crust turns red. It heals slowly and may leave scar after it heals.
Boil
Boils are bacteria skin infection of hair follicles. It also involves surrounding tissues. It can occur in any part of the body with hair follicles. That means boil cannot form under the sore of the feet or palm.
Also called furuncles, it is common in the face, neck, thigh and buttocks. It looks like an inflamed red bump. When it ruptures, cloudy fluid or pus drains out. A group of boils is called carbuncle.
 |
| Boil |
Symptoms
It begins like a benign looking bump (pimple). It later becomes hard and painful. The pus forms as a result of immune response. The pus puts pressure on the bump that causes it to burst. It results in red, swollen and tender scarring. Rarely fever and chills.
Causes
It is caused by staphylococcus aureus. There are over 30 known species that cause boil especially methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Resistant boils can lead to complications such.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Boil
It is self limiting and goes on its own after draining. Use of warm compress to speed up the draining process. Amoxicillin, ampicillin, cefazolin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cephalexin, clindamycin, amikacin, doxycycline, erythromycin, gentamicin, levofloxacin, mupirocin, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim or tetracycline are antibacterial of choice. They should be paired with antiinflammatory drugs like NSAIDS.
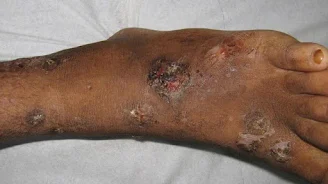
Leprosy
Leprosy is an old disease reported by ancient historians including the Bible. It is caused by mycobacterium leprae. It is also called Hansen disease. It is a chronic disease that affects the nerves of the extremities, skin, nose and upper respiratory tract.
Symptoms
1. Muscles weakness
2. Numbness of the hands, arms, legs and feet
3. Skin lesion. The skin lesion decrease the sensation to touch, temperature and pain
Complications
Of all the bacteria skin disease, it is the most dangerous. It produces sun ulcer, nerve damage in arm and legs, nosebleed and nasal congestion, collapse of the nasal septum, iritis, glaucoma, blindness, erectile dysfunction, infertility, kidney failure, etc. It can cause severe disfigurement and disability.
Mode Of Transmission
It is not highly contagious. It is transmitted through the cough and sneeze of an infected person. But it has to be prolonged contact. Incubation period is about five years. Symptoms may not appear for up to 20 years.
Types
The classification is based on individual immune reactions.
Tuberculoid: exhibits few lesions with mild symptoms. They are mildly contagious and found with those with high immunity. They are less contagious.
Lepromatous: affect skin, nerves and other organs. There are widespread lesions including nodules (large lumps and bumps). They are more contagious.
Borderline: these have clinical symptoms and characteristics that falls in-between both.
Read Also: Vaccine programme in Nigeria
The world health organisation (WHO) gave their own classification. They are paucibacillary and multibacillary.
Paucibacillary has five lesions or fewer. While multibacillary has lesions more than five with bacterium in skin smear or both.
Ridley-Jopling has another reclassification. It follows minor to more severe. They are tuberculoid, borderline, mild borderline, borderline lepromatous and lepromatous. From their description, intermediate leprosy was missed.
 |
| Leprosy |
Diagnosis
Biopsy or lepromin skin test
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Leprosy
The WHO recommended combination therapy for both types of leprosy. For paucibacillary, rifampicin and dapsone orally is the drug of choice. For multibacillary leprosy, a three drug combination of rifampicin, dapsone and clofazimine is the drug of choice. Steroids, aspirin or thalidomide help with inflammation. Treatment is for one to two years. Other antibiotics that can be used are ofloxacin and minocycline.
Dosage of rifampicin is 600mg monthly orally and 50mg daily. Clofazimine is 399mg once monthly and 50mg diay. Dapson is 100mg daily orally.
Note: FOTO credit to healthline.com

Comments
Post a Comment
Please have your say