Clinical Pharmacy And Pharmacy Administration (PCA) Full Curriculum
Clinical pharmacy and pharmacy administration (PCA) is one of the most simple departments in pharmacy school. It is a unique department building a bridge between all the other departments. It unites all the departments in pharmacy school. Everything you studied from the other departments is put into use here. It builds the pharmacy student into a fine pharmacist.
It is divided into management and clinical. The clinical aspect focuses on how the student can practice as a pharmacist in hospital and community service and what is expected as a pharmacist from the society. The management aspect shows how the pharmacist can practice his clinical role and still make decent income using managerial skills. The department had the highest number of lecturers including professors of high calibre.
PCA Course Outline
The courses begin in year two in most pharmacy schools. However, don't be surprised when it begins in year three or four in others. Some of the courses may be very short and others very bulky. It all depends on the school curriculum. When the topics in one course are bulky, it is mainly because most topics compress into few and happen in schools the course begins in year four.
Year two began with introduction to pharmacy as a first semester course. This course is interesting. Here you will learn about how pharmacy began and when it started to divide and the various stages of pharmacy practice over the century. It will also elaborate on the introduction of pharmacy in Nigeria. The meaning and definition of terms is not left out. The meaning of symbols and logos used in pharmacy and their origin. I always remember the name asklepios because it was a funny name of a god one of the symbols of pharmacy was named after.
Computers in pharmacy is another interesting and simple course, especially if you have already done computers course before. There is nothing special about it. Just a definition of terms and their meaning. List some hardwares like hard disk and motherboard and what they do and how important softwares is to pharmacy practice. The importance of moving from analogue to digital is just the bottom line of this course. And funny enough, most of the professors lecturing things like this are still using analogue methods in their office. Lol. And this may come in the first semester too.
The second semester of year two was a turning point. There we came across statistics in pharmacy. Statistics is basically a science that involves data collection, data interpretation and finally, data validation. I used to think that statistics end with mean, median and mode. But when we got deeper, I was lost. Infact, standard deviation was now a simple topic in statistics. They were just touching different statistical analysis methods used in analysing data. Regression, sample size determination and hypotheses testing are some others that were touched. For some time, we felt we didn't need it. But we later realised that most of those statistical analysis methods were needed to analyze some of our project work, be it in the department or other departments. I use one to analyse my data in my pharmacognosy and traditional medicine project.
Year three came with a bang. Infact, it was medh o. Every department has at least one difficult course and in PCA, that is jurisprudence in pharmacy. Others call it forensic pharmacy and pharmacy ethics. This course covers all pharmacy laws, drug rules and regulations, pharmacy and drug related decrees and acts promulgated by the federal government of Nigeria. That is not all. The course list registered pharmaceutical organizations and their functions. Let me not forget about the national drug policy, national drug formulary, essential drug list, pharmacy ethics and pharmacist council decree. Others are poisons and pharmacy acts, counterfeit and fake drugs (miscellaneous poison act), patent and proprietary medicine vendors license, drug advertisement, NDLEA decree, Indian hemp decree, the dangerous drug acts, NAFDAC decree, the food, drugs and cosmetic acts and drugs and related products registration decree.
Coming to the second semester, the first course that kind of introduced us to pharmacology was biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics. This course is all about how drugs are absorbed, distributed and eliminated (metabolism and excretion) from the body. The bottom line is how a drug of a particular physicochemical property behaves in a route of administration. That is the bioavailability of the drug after passing through different routes and what happens if the physicochemical properties of the drug are changed. This is pharmacology but the explanation is on how it can be put into real life use. For example, with this you can adjust the dose or dosage route for different persons when you know about the pharmacokinetics of the drug. Something this course also teaches you is how to study the different routes of drug administration and their pathways including metabolism. How raw data can be used to derive drug parameters and models that best describe the process of drug absorption, distribution and elimination. Look out for the different models of drug pharmacokinetics such as the compartment method (single and multiple model). These models are used to explain how drugs behave in the body. Also, the pharmacokinetics of multiple drugs regimen and also of sustain release dosage form. The design of many dosage forms is based on their pharmacokinetics parameters. Some drugs are only liquid and not in tablet form. Example is cough syrups. The decision to make them as syrup and not tablets is because of their pharmacokinetics data. This however influences pharmacological response through their pharmacokinetics parameters.
To be able to clerk a patient and counsel, you need clinical knowledge. However, to be able to extract details from the patient and tell the patient want to do, you need communication skills. Not as easy as it seems, this course most likely in year four beginning in first semester will expose students to different techniques of asking questions and the type of questions to ask and avoid. It is called communication skills and drug information evaluation. Aside from communication with patients, pharmacists also need these communication skills when talking to other health care professionals. Patient data must be kept private and stored properly which should never be disclosed to the wrong person. This involve proper documentation and safe keeping. But when we talk about drug evaluation in hospital setting, we are talking about the development of formulary and essential drug list. In community pharmacy setting, we are talking about how to use drug literature to find information about the right drugs and manage minor ailments. It is also essential to carry out primary care to patients on chronic conditions established by the physician. Lastly, educate patients on drugs, disease and supplement. A little laboratory work is done here on how to measure vital signs.
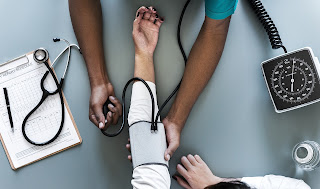 |
| Vital signs |
Second semester of that year four can be filled up with many courses. It may just be one or two. However, one course that is very suitable for year four is roles of pharmacist in management and administration of retail and hospital pharmacy such as drug controller. The focus is on the pharmacist to manage and organise the hospital or retail pharmacy. These include drug selection, stocking, stock keeping, planning, and execution. Some managerial skills that are not tangible like motivation through inspiration.
Read Also: Clinical pharmacy and pharmacy administration project
Read Also: Clinical pharmacy and pharmacy administration project
Another course will focus on how to start a community or retail pharmacy in line with the laws of the federation. It will also talk about what are the duties of a pharmacist in the hospital and community pharmacy. The location and design layout of the pharmacy space is spelt out such as distance between two community pharmacies and all that. Finally, where can pharmacist source for fund or capital for investment is very important. It will include some advantages and disadvantages for each source.
Year five is designed to cover clinical pharmacokinetics. This was close to real life experience. It is at this stage we started to feel pharmacy as a practice oriented profession. All the previous years, what we have been seeing looks abstract. This was where we talked about pharmaceutical care and the different stages of pharmacy practice and pharmaceutical models. How pharmaceutical care began and its definition. There were different disease conditions, how the disease affected drugs and the best way to handle it. It is how a disease modifies body function. From erldely to children down to pregnant women and lactating mothers, it covers it all. It is in this course that more emphasis was laid in individualized dosage form. Everything would not be complete if we did not talk about how to identify and resolve drug therapy problems.
There is this clinical clerkship programme called externship pharmacy students participate in final year. Some schools run it throughout year five but others use holidays periods. It is a clinical rotation in a teaching hospital. Each student goes on a ward round with the medical team to scrutinize each patient's datas along with their drugs for correctness. If all the drugs are in line, the drug is dispensed with counselling. What students look out for in a prescription is using past medical history and present conditions to access compatibility of drugs, signs and symptoms of drug toxicity, etc.
There is a pharmacy project and industrial training (IT) in the curriculum. For the project, it is in year five and begins from the first semester. As for IT, it can be during the second semester of year three holiday or the whole of first semester year four.
Share On Social Media With Family And Friends To Show You Care!
Drug evaluation
ReplyDelete