Advantage And Disadvantage Of Intradermal Injection
Intradermal injections (ID) are injections administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. The ID injection route has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. These types of injections are used for sensitivity tests, such as TB.
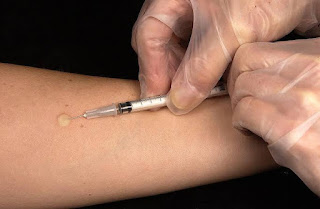 |
| Intradermal injection |
The most common sites used are the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. The dosage of an ID injection is usually under 0.5 ml. The angle of administration for an ID injection is 5 to 15 degrees. Once the ID injection is completed, a bleb (small blister) should appear under the skin. Method of administration is the Mantoux procedure and intradermal needles.
Read Also: Overview Of Intramuscular (IM) Injection
Equipment used for ID injections is a tuberculin syringe calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a millilitre, and a 1/4 to 1/2 in., 26 or 27 gauge needle.
Advantages Of Intradermal Injection
1. Improve vaccine efficacy
2. Dose-sparing strategy during shortage
3. Reduced cos
4. Overcome poor-response (e.g. elderly or
immunocompromised
Read Also: Overview Of Intradermal Injection
Disadvantages Of Intradermal Injection
1. Skin holds limited volume--optimal dose is
not know
2. ID injection technique requires skill and tim
3. Injection site reactions--discolouration
swelling, itching
4. It is painful
5. Only a small amount of the drug can be administered

Comments
Post a Comment
Please have your say