Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Fungi Skin Infection
Fungi (yeast or mould) skin infections are skin conditions caused by one or more fungus. They affect people of all ages and can affect one or more skin layers. In worse situations, they enter the bloodstream.
The skin is the largest organ in the body. It is also the first line of defence against infection. The skin is made up of layers. They all have different functions.
The epidermis is the first layer of the skin outside. It protects the body against different forms of fungi from the surrounding. The dermis is the next layer which provides nutrition for the epidermis. The subcutaneous tissue is the last layer which acts as a shock absorber for the skin, stores energy and regulates body temperature.
Causes Of Skin Infection
There are fungus in the air and the surrounding. There are fungus on the skin. However, the skin is safe as long as the skin is not broken. Fungi can enter the skin from cuts or when there are allergic skin diseases such as eczema. In some cases, large fungi colonies in the skin can cause skin infection.
A fungi that gains access into the skin will do well to migrate to the layer with the best condition and start to multiply. This multiplication results in an increased need for more nutrients from under the skin and more space. This leads to different types of skin condition.
Fungi Skin Infection
There are thousands of species of fungi that can cause skin infections. Some can cause more than one type of infection. But it is easy to diagnose a fungi skin infection from other types of skin infection.
Read Also: Treatment for different virus skin infection
Fungi skin infection often presents with small or large blisters coupled with severe itching. Fungi often grow in warm, moist environments. Body chemistry and lifestyle can increase the risk of a fungal infection. Wearing sweaty or wet clothes is a risk factor for fungi skin infections. They are most likely to develop in damp areas of the body, such as the feet or armpit.
Treatment often consists of topical cream, spray, lotion or ointments. Severe cases rarely occur. But if they do, oral antifungal does the work. Some may require minor surgery. Some fungal infections aren’t contagious, and these infections are typically non-life-threatening.
Diagnosis/Test
Fungi skin infection can be diagnosed by merely doing skin examination. The room should be well lit and without shadow. The area of the body uncovered and the skin examined with a magnifying len.
Last resort is to request for a laboratory diagnosis. Most fungi skin infections can be diagnosed without it.
Types Of fungi Skin Infection
There are different funguses that cause skin infections. They are classified under five categories.
Athlete's Foot
Is also called tinea pedis. It affects the sole of the feet and palm. It can also spread to the toenails through in-between toes. It is common among diabetes and immunocompromised patient caused by disease, drugs or lifestyle like smoking.
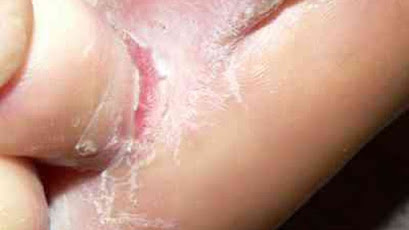 |
| Athletes foot View gallery for more images |
Symptoms
Under the skin become dry, itchy, stinging and burning with blisters that peel. This feeling can also spread to in-between toe. It will eventually crack and start peeling off.
When it spreads to the toenails, toenails become discoloured, thick and crumbly. The toenails eventually pull away from the nail bed.
Types of athlete's foot
- Interdigital. This is also called toe web infection. Most people with athlete’s foot have this form. It usually occurs between your two smallest toes. The infection can spread to the sole of your foot.
- Moccasin. This form can begin with irritation, dryness, itching, or scaly skin. Over time, your skin may thicken and crack. This infection can involve your entire sole and extend onto the sides of your foot.
- Vesicular. This is the rarest kind of athlete's foot. It usually begins with a sudden outbreak of fluid-filled blisters, often on the underside of your foot. They also can appear between your toes, on your heel, or on top of your foot... WebMD
Causes
The tinea pedis thrive in warm, moist environments like the bathroom and swimming pool. Prevention is wearing bathroom slippers or loose shoes in public bathrooms and swimming pools. Avoid sharing towels, shoes and socks. Keep feet dry at all times. Treat foot injury immediately. Wash clothes and shoes with soap and warm water (60°c). Sterilise all manicure and pedicure equipment.
Diagnosis
Microscopic examination of the skin lesion using potassium hydroxide (KOH). The skin is scraped and placed in KOH. The KOH destroys normal cells leaving infected cells which can be viewed in a microscope.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Athletes Foot
Treatment involves the use of topical antifungal applied on the affected skin morning and night for a long time. Applications continue even after at least two weeks of clearing off. This is to prevent recurrence. Suitable topical antifungal are:
1. Miconazole
2. Terbinafine
3. Clotrimazole
4. Butenafine
5. Tolnaftate
Oral antifungal can be added to speed up the process such as:
1. Fluconazole 50-200mg daily for the duration
2. Itraconazole 100mg daily for the duration
3. Terbinafine
There is a need for topical or oral steroids to handle the inflammation and itching. Adding antibiotics is necessary in case of secondary infection. Athletes' foot does not result in complications but rare cases do occur. It happens when there is a secondary infection due to tinea pedis. Treatment for secondary infection should be initiated immediately if the foot is swollen, feel painful, hot with pus and fever.
Home remedies include soaking the foot in salt warm water or dilute vinegar to help dry up the blisters before applying topical creams. Applying the cream directly on the affected part for the first time will prolong the duration of treatment. After bathing and treatment about to be initiated for the first time, the leg should be left moist. Table salt should be applied on the affected place. Apply pressure using the hand and scrub the upper skin layer of the affected part with the table salt. Those whitish layers will start to fall off. Scrubbing should be stopped when it has gotten to the uninfected skin layer and starts feeling pains. Now it is time to start application of the medicated cream.
Prevention involves using shoes or socks made of breathable fibres such as cotton and wool. Change socks when damp Keep the legs always dry and avoid using barefoot in public places.
Yeasts
Yeast (candida) is a fungus that occurs naturally in the body. Excess growth leads to yeast infections. It affects mostly women. 3 out of 4 women will experience it in their lifetime. It can appear in any part of the skin. It is called cutaneous candidiasis.
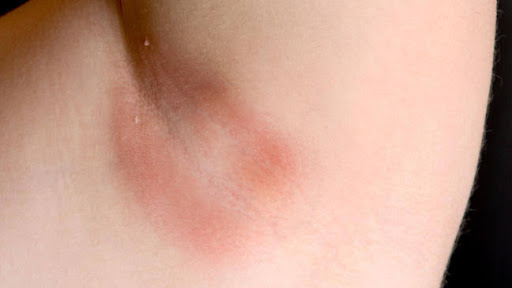 |
| Yeast skin infection |
Symptoms
The major symptom is itchy vagina which can lead to irritation. Very serious cases lead to vagina discharge. The discharge can have different colours like white to yellowish. If it appears in other parts of the body, it causes itching. It can cause diaper rash, oral thrush and nail infection.
Causes
Anything that enhances the growth of yeast in the body such as antibiotics. Most antibiotics destroy lactobacillus bacteria that keeps yeast proliferation in check. Others are hormonal changes during pregnancy and period, birth control pills, sexually transmitted infection (STI) and diabetes.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Yeast
The use of antifungal creams, ointment or suppositories is the main treatment option. They are clotrimazole, econazole nitrate, ketoconazole or miconazole and terbinafine. Nystatin is another alternative. Clotrimazole 100mg, Nystatin and miconazole can be used daily at night for three or six days. The duration is dependent on the severity. Systemic approach is adopted when it is refractory candidiasis. Triazole derivatives is the drug of choice which includes fluconazole for systemic infection. Oral terbinafine is not recommended for refractory candidiasis. Fluconazole can be taken 150mg daily for 10 days.
Unapproved treatment is the use of boric acid. Boric acid is an antiseptic and antifungal suppository. There are individual report about its effectiveness.
Prevention is avoiding anything that will alter the normal flora of the vagina. Unfortunately, some of the causes cannot be avoided. However, avoid douching, scented tampons, pads, soaps, detergent. Wear cotton, nylon or polyester underwear. Take more probiotics such as yoghurt.
Ringworm
The name ringworm may sound like a worm infection. But that is not the case. The name is given to this disease because the fungi tinea that causes it forms a ring on the skin that looks like a worm. This infection is also called dermatophyte or dermatophytosis.
The name ringworm tinea can affect the body (tinea corporis), scalp (tinea capitis), feet and palm (tinea pedis) or the groin (jock itch, tinea cruris). Other areas it affects are the nails and beard.And it is common among humans and animals.
 |
| Ringworm Image gallery of ringworm |
Symptoms
It usually begins with a white patch that starts to spread in the skin. As it spreads, the center brgin to have a clear skin colour while the edges form a ring that is thicker or raised bumps with red lines. The infected part is scaly and itchy. The ring can be red.
When it affects the nail, the nail becomes thicker or crack or discoloured. The hair in the scalp can fall off when the head is affected.
Stages
1. Dry and scaly skin patch with red or pink patches
2. It begins to spread outward leaving normal skin at the center
Causes
Three organisms have been implicated which are Trichophyton, microsporum and epidermophyton. They thrive in dead tissue. They are very contagious and can spread through sharing of combs, towels, hats or pillows. It is very common among children.
Diagnosis
To diagnose ringworm, black light or wood lamp is used. Ringworm glow or fluorescence under black light. Another method is the use of skin biopsy with potassium hydroxide (KOH) or cell culture.
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Ringworm
There are topical and oral medications for ringworm. Using one alone may not be fast enough. In most cases, topical and oral are combined.
Approved creams, ointment, sprays, gels or powder for treating ringworm are clotrimazole, miconazole and terbinafine. It is always good to apply it to spread over the infected area.
Tablets that work in ringworms are griseofulvin and terbinafine. They are very important for ringworm especially those under the nail or scalp as it is difficult for cream to access those places well. Griseofulvin 500mg can be taken morning and night for adults. Children dose can be adjusted according to weight.
Shampoos such as selenium sulfide are not for treatment as they only stop the spreading of the ringworm. They are useful when oral antifungal is used along with it. Treatment lasts for at least six weeks.
Avoid oral ketoconazole and miconazole in pregnancy. Ciclopirox, clotrimazole, naftifine, oxiconazole and terbinafine can be used instead. Griseofulvin and terbinafine is known to cause diarrhea, stomach upset, high fever, etc.
Prevention is simple. Avoid infected animals. Wash infected clothes and avoid contaminants. Avoid sharing items such as combs.
Nail Infection
Nail infection is called onychomycosis. They are also called tinea unguium. They affect both toe and fingernails but more especially toenails. It can be caused by the same fungi that is responsible for ringworm. It is more common in adults and men.
Types
Distal lateral subungual: this type present with a white or yellow streak across the nail. The outer edge of the nail has a jagged appearance.
White superficial: the top layer of the toenail comes under attack from the fungi. This leaves well defined white spots or patches on the nail. It affects the entire nail and makes it rough, soft and prone to crumbling. Spots on the nail may become pilted and flaky. It affects only toenail.
Proximal subungual infection: it begins from the base of the nail as a yellow spot and continues to spread upward.
Candida yeast infection: this type is caused by a prior infection or injury of the nail. It could also be as a result of regularly soaking the hands in water. The cuticles around the nail begin to swell, feel tender to touch and appear red in colour. Eventually, the nail itself may lift off the nail bed or in worse scenario, fall off completely.
Classification
Endonyx onychomycosis: this type affect the interior of the nail plate and never the nail bed
Totally dystrophic: this is end stage distal or proximal subungual. The nail bed is thick and raised with a copious keratotic debris
Fungal melanonychia: this is caused by scytalidium, alternaria or exophiala. The nail plate is disfigured turning it brownish or blackish. May present similar to subungual melanonychia.
 |
| Nail infection Source: mayo clinic |
Symptom
The nail becomes discoloured. It appears either in yellow, brown or white in colour. The nail becomes distorted and becomes thick, fragile and crack (brittle). It can smell but not painful. Compication is nail deformity.
Risk Factors
Fungi thrive in moist, warm environments. Also, persons with poor blood circulation are prone to nail infection. Injury and contact with infected persons or objects can expose one to the infection. Others are diseases such as diabetes and boils, people above 65 years of age, use of public pools or bathroom without slippers, weak immunes system from disease, drugs or lifestyle such as smoking.
Diagnosis
1. Periodic-acid-schiff staining
2. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) staining and microscopy
3. Sabouraud/dermatophyte medium test
4. Further laboratory test may be needed
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Nail Infection
There are suitable treatments for nail Infection. Oral antifungal agents such as terbinafine, itraconazole, fluconazole and griseofulvin are very effective. Cream may not be necessary as it finds it hard to get into the nail because of its nature.
Prevention involve using good shoes and socks all the time. Reduce hands and legs getting wet.
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is the name given to the mouth infection also called oral candidiasis, oropharyngeal candidiasis or simply thrush. The causative organism is a yeast. It is common in infants and toddlers.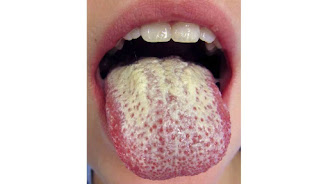
Oral thrush
Image gallery
Symptoms
The first symptoms begin on the inner cheek. A yellowish bump is formed in the inner cheek. Other parts affected by this colouration are the tonsils, gums, lips and tongue.
Read Also: Treatment for bacteria skin infection
Other symptoms include bleeding from a scrap bump, soreness or burning of the mouth, difficulty swallowing, bad taste in your mouth and loss of taste. It is rarely serious. However, complications can arise especially in immunocompromised people as it spreads to other parts of the body. Systemic candidiasis leads to septic shock.
Cause
It is contagious and spread through kiss, vagina and oral sex, childbirth and breastfeeding. It is caused by a fungus known as candida albican. Risk factors include the indiscriminate use of antibiotics, corticosteroids inhalers, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Diseases such as leukaemia, diabetes and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) predispose people to oral thrush. Lifestyle such as smoking cigarettes and dentures can contribute.
Diagnosis
1. Biopsy
2. Throat swab and culture
3. Endoscopy
Pharmacotherapy/Treatment Of Oral Thrush
There are effective oral drugs that treat oral thrush. They are fluconazole, clotrimazole lozenges, nystatin mouthwash, itraconazole and amphotericin B. They effectively take care of oral thrush within a couple of weeks.
After treatment, change the toothbrush and replace with a soft toothbrush. Avoid the use of antibacterial mouthwash as it destroys the moth normal flora and predispose one to oral thrush. Anything to restore the mouth normal flora is welcome such as washing the mouth with salt water or water and baking soda, lemon juice or apple cider vinegar. Yoghurt can also help.

Comments
Post a Comment
Please have your say